
SLO-Aware Cellular Multi-Access Edge Computing
Practical, SLO-aware resource management for 5G multi-access edge computing
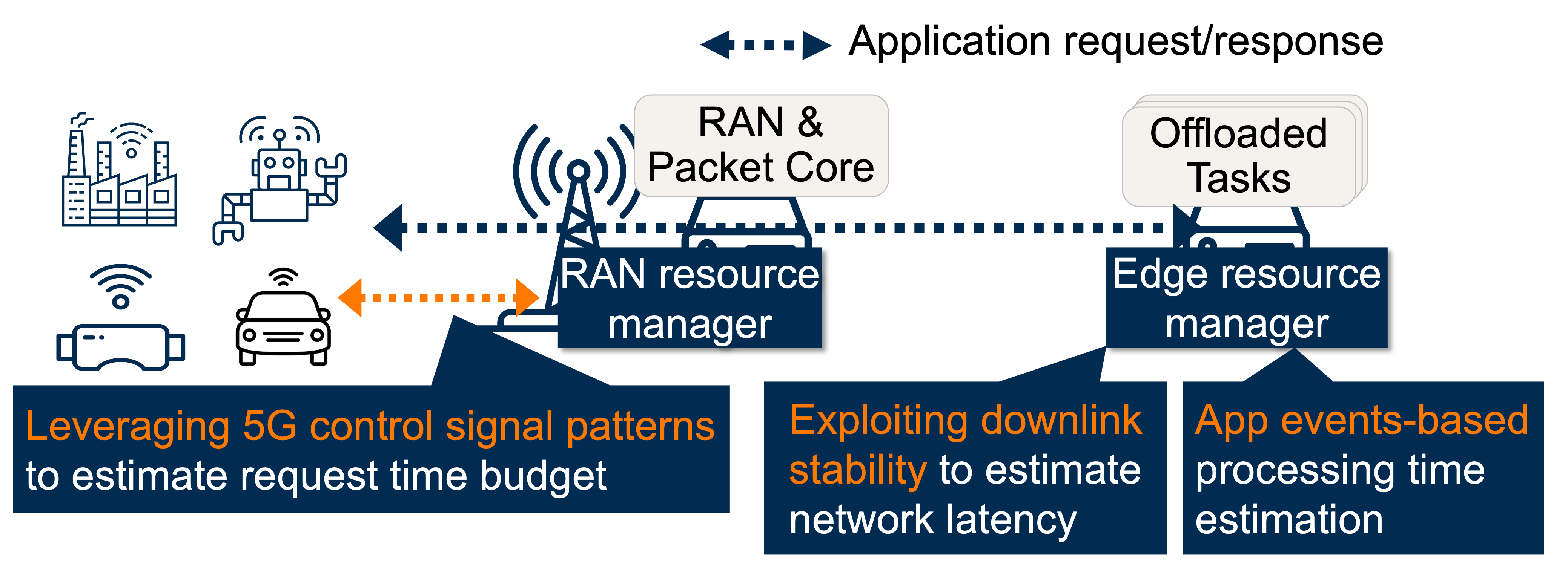
While multi-access edge computing (MEC) promises low-latency support for applications, our measurements on various commercial deployments reveal a different reality: high tail latencies frequently violate application SLOs. The culprit? Resource contention at both the RAN and edge servers, compounded by schedulers that lack SLO awareness. Existing solutions require tight coordination between RAN and edge, which is impractical when different entities operate each component (e.g., Verizon runs the RAN while AWS provides edge compute). Even if such coordination were possible, feedback delays prevent timely resource allocation.
SMEC takes a different approach: it brings SLO-aware scheduling to MEC through completely decoupled resource managers at the RAN and edge, each making deadline-aware decisions independently.
Our core insight is that standard 5G protocols and MEC application behaviors already expose the signals needed for SLO-aware scheduling without requiring RAN-edge coordination. SMEC exploits these readily available signals through three key ideas:
- Exploiting 5G control signals for request identification at the RAN: Standard 5G control signaling between UE and base station naturally exhibits distinctive patterns when new application requests are generated. SMEC leverages them to detect request boundaries at the RAN without payload inspection or protocol modifications.
- Leveraging downlink stability for network latency estimation at the edge: 5G downlink transmissions exhibit more predictable latency than uplink. SMEC exploits this asymmetry through a lightweight probing protocol between edge servers and client devices, enabling accurate latency tracking without RAN-edge coordination.
- Utilizing application lifecycle events for processing time prediction at the edge: MEC applications' request-response behaviors expose key lifecycle events that enable processing time estimation. SMEC tracks these naturally occurring events through server-side APIs and builds execution history, providing sufficient accuracy for deadline-aware scheduling without requiring invasive application changes.
-
Open-source Implementation
RAN resource manager: Pluggable scheduling module for srsRAN's MAC layer
Edge resource manager: User-space daemon managing CPU and GPU resources with lightweight client-side timing daemon
-
Evaluation Highlights
90–96% SLO satisfaction across real-world latency-critical applications with SLO requirements ranging from 10s to 100 milliseconds
Starvation-free for best-effort applications sharing remaining bandwidth
BibTeX
If you find SMEC relevant to your research, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{smec-nsdi26,
title = {Enabling SLO-Aware 5G Multi-Access Edge Computing with SMEC},
author = {Xiao Zhang and Daehyeok Kim},
booktitle = {Proceedings of 23rd USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation {(NSDI)}},
year = {2026}
}
Contact
Xiao Zhang (zx123@utexas.edu)
Daehyeok Kim (daehyeok@utexas.edu)
Sponsors

